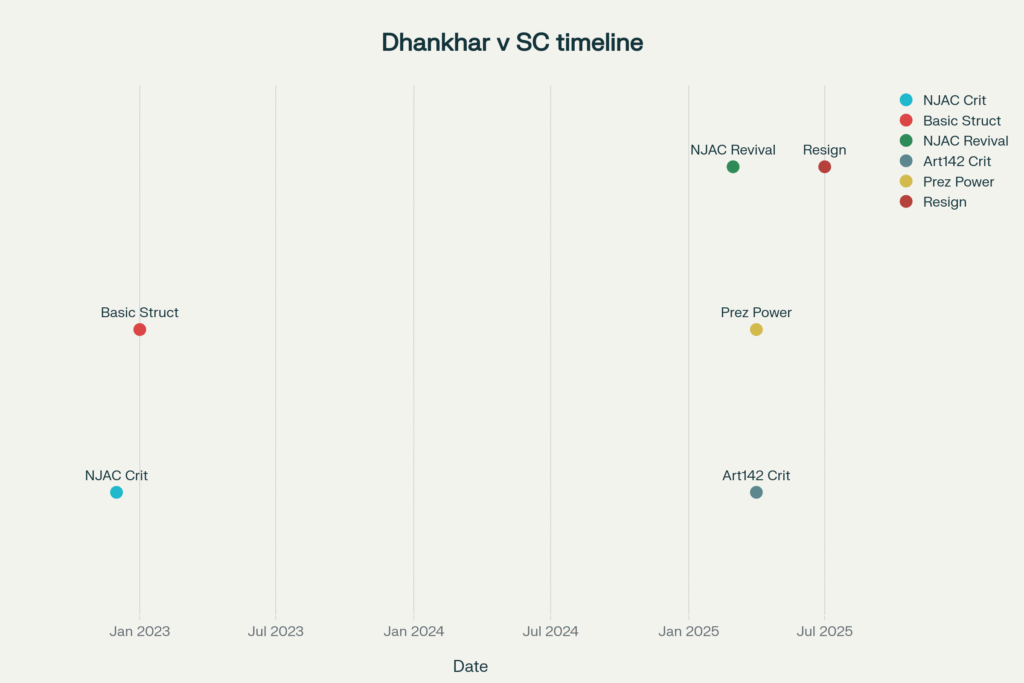
Vice President Jagdeep Dhankhar’s resignation surprised the nation from his constitutional post on Monday evening. However, his departure marked the end of a tenure filled with controversy. Throughout his time as Rajya Sabha Chairman, he consistently questioned the Supreme Court’s decisions. His criticism spanned from the NJAC Act to the Basic Structure doctrine.
The Beginning of Constitutional Confrontation : Jagdeep Dhankhar’s resignation
Jagdeep Dhankhar’s resignation came after years of challenging judicial supremacy. In December 2022, he began his term with bold statements against the judiciary. Moreover, he called the Supreme Court’s 2015 NJAC verdict a “glaring instance” of parliamentary compromise. Furthermore, his remarks set the tone for ongoing constitutional battles.
The NJAC Act represented a significant attempt at judicial reform. Parliament passed this legislation with unprecedented support in 2014. Nevertheless, the Supreme Court struck it down in 2015. Consequently, Dhankhar viewed this as an attack on parliamentary sovereignty.
Read More : WI vs AUS T20: Green and Owen Shine in Thriller

Understanding the NJAC Controversy Behind Jagdeep Dhankhar’s Resignation
The National Judicial Appointments Commission aimed to transform judicial appointments completely. Previously, the collegium system allowed senior judges to select their successors. However, the NJAC proposed a different approach entirely.
Structure of the NJAC System
The proposed commission included six members with diverse backgrounds. First, the Chief Justice of India served as chairperson. Second, two senior Supreme Court judges participated as members. Third, the Union Law Minister represented the executive branch. Finally, two eminent persons brought external perspectives to the process.
This structure promised greater transparency than the existing collegium system. Additionally, it aimed to reduce nepotism in judicial appointments. However, critics worried about executive interference in judicial independence.
Why the Supreme Court Rejected NJAC : Jagdeep Dhankhar’s resignation
Justice J.S. Khehar’s majority opinion raised several constitutional concerns. Initially, the court worried about executive dominance in judicial appointments. Subsequently, it identified potential conflicts of interest involving the Law Minister. Furthermore, the veto power structure created problematic scenarios.
The court particularly criticized the “eminent persons” concept. These individuals lacked defined qualifications or expertise requirements. Moreover, their selection process remained vague and potentially arbitrary. Ultimately, the court deemed this insufficient for constitutional appointments.
Read More : School Lunch Tragedy : 9-Year-Old Dies After Cardiac Arrest
Basic Structure Doctrine and Jagdeep Dhankhar’s Resignation Debate
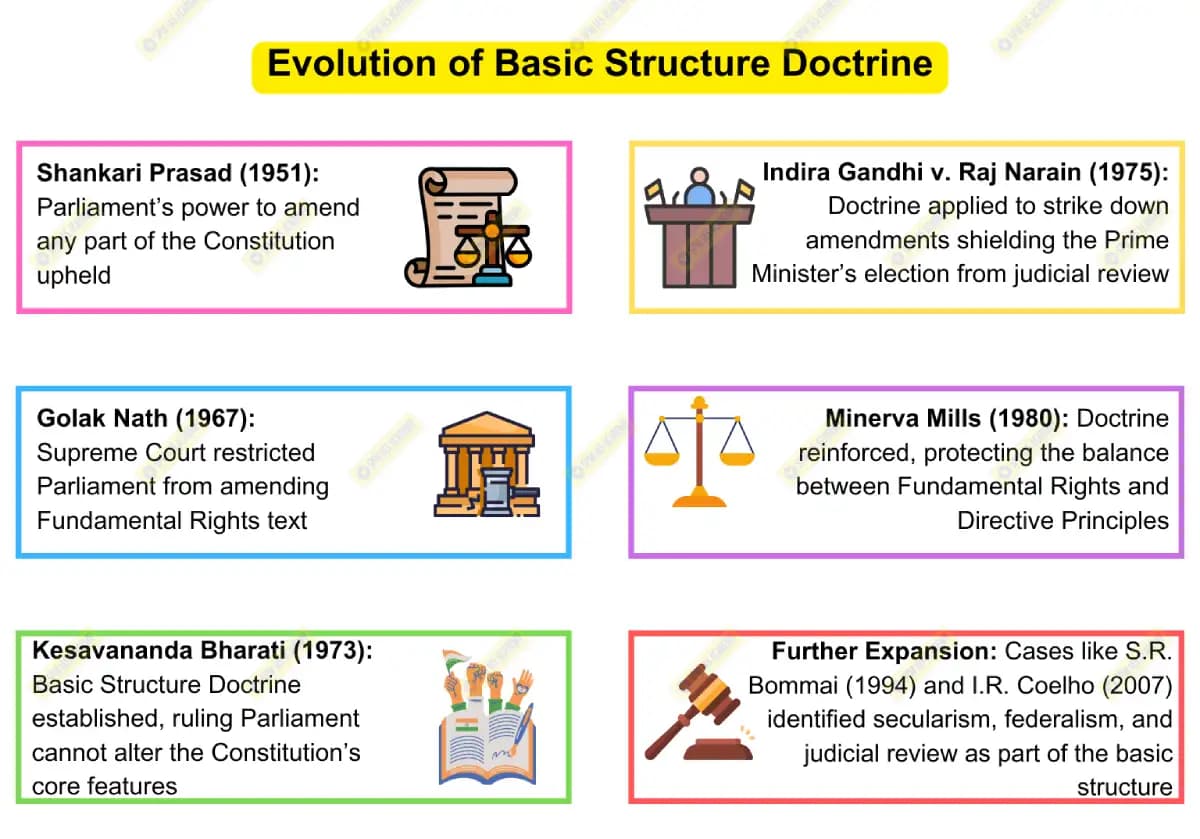
Dhankhar’s most controversial statements targeted the Basic Structure doctrine itself. In January 2023, he questioned the Kesavananda Bharati judgment directly. Specifically, he called it a “bad precedent” that compromised parliamentary sovereignty.
Evolution of Basic Structure Principle
The doctrine emerged from the landmark 1973 Kesavananda Bharati case. This judgment established that certain constitutional features cannot be amended. These include democracy, secularism, federalism, and judicial review. However, Dhankhar argued this limited Parliament’s legitimate authority.
The doctrine protects fundamental constitutional principles from majority tyranny. It ensures that temporary political majorities cannot destroy democratic foundations. Nevertheless, critics like Dhankhar see this as judicial overreach.
Elements Protected by Basic Structure
Several constitutional elements enjoy basic structure protection. The supremacy of the Constitution stands as the primary feature. Democratic governance and republican principles also receive protection. Furthermore, the separation of powers remains inviolable.
Individual freedoms and fundamental rights constitute core elements too. The federal character of the Constitution cannot be destroyed. Additionally, the rule of law and judicial review maintain constitutional status. These elements collectively preserve India’s democratic identity.
Read More : BluSmart Cab Disaster: From Trust to Fraud
Article 142: The Nuclear Missile Controversy
In April 2025, Dhankhar launched his sharpest attack on judicial power. He described Article 142 as a “nuclear missile against democratic forces.” This provision grants the Supreme Court extraordinary discretionary powers.
Understanding Article 142’s Scope
Article 142 allows the Supreme Court to pass any order ensuring “complete justice”. This power enables the court to override existing laws when necessary. Moreover, it can fill legal gaps to resolve disputes comprehensively. However, Dhankhar viewed this as excessive judicial authority.
The article traces its origins to colonial legislation. Section 210 of the Government of India Act 1935 provided similar powers. However, its modern application has expanded significantly over decades.
Read More : Free Perplexity Pro, Grab for a Year on Airtel
Dhankhar’s Concerns About Presidential Direction
The Vice President particularly criticized courts directing the President on bill assent. In April 2025, the Supreme Court set a three-month deadline for presidential decisions. Consequently, Dhankhar questioned this constitutional interpretation.
He argued that courts could only interpret the Constitution under Article 145(3). Moreover, such interpretation requires benches of five or more judges. Therefore, he deemed the presidential direction constitutionally improper.
Parliamentary Sovereignty Versus Judicial Review
Dhankhar consistently championed parliamentary supremacy throughout his tenure. He argued that elected representatives should determine constitutional content. Furthermore, he believed Parliament represents the people’s sovereign will directly.
Read More :iPhone 17 Air Launches September: Ultra-Slim Revolution
The Democratic Legitimacy Argument
Dhankhar emphasized Parliament’s electoral legitimacy repeatedly. Unlike judges, parliamentarians face regular elections and public accountability. Moreover, they directly represent constituency interests and popular will. Therefore, he argued their authority should remain supreme.
This perspective reflects classical theories of democratic governance. In many democracies, legislative supremacy remains the dominant principle. However, India’s constitutional structure includes judicial review as a check.
Read More : Trump claims jets downed amid India‑Pakistan Operation Sindoor
Judicial Response to Dhankhar’s Criticism
Chief Justice D.Y. Chandrachud defended the basic structure doctrine vigorously. He called it a “north star” guiding constitutional interpretation. Moreover, he praised its adoption by neighboring countries like Pakistan and Bangladesh.
The judiciary argued that constitutional supremacy transcends parliamentary authority. While Parliament can amend most constitutional provisions, basic structure limitations protect democracy itself. Furthermore, these limitations prevent tyranny of the majority.
The NJAC Revival Attempts Following Jagdeep Dhankhar’s Resignation
Even after his departure, the NJAC debate continues to influence judicial appointments. In March 2025, cash discovery at a judge’s residence reignited reform discussions. Dhankhar immediately connected this incident to NJAC’s absence.
Current Collegium System Challenges
The existing collegium system faces persistent criticism regarding transparency. Decisions occur behind closed doors without public explanations. Moreover, allegations of nepotism and favoritism persist regularly.
Gender representation remains particularly problematic in current appointments. Only four women judges currently sit in the Supreme Court. Additionally, the system struggles with persistent judicial vacancies nationwide.
Proposed Reforms and Future Directions
Legal experts suggest various reforms to improve judicial appointments. Enhanced transparency in collegium decisions represents one priority. Moreover, broader eligibility criteria could increase diversity significantly.
Some propose hybrid systems combining collegium and executive input. These models might address both independence and accountability concerns. However, constitutional amendments would likely face judicial scrutiny again.
Impact on Constitutional Democracy
Dhankhar’s sustained criticism created unprecedented constitutional tensions. His statements challenged traditional separation of powers principles. Furthermore, they raised questions about institutional respect and cooperation.
Separation of Powers Under Strain
The confrontation highlighted fundamental constitutional tensions. Executive leadership directly challenged judicial authority and interpretation. Moreover, this conflict extended beyond normal inter-institutional disagreements.
Constitutional experts worried about democratic stability during this period. Sustained attacks on judicial legitimacy could undermine rule of law. Furthermore, they might encourage similar challenges from other institutions.
International Comparisons and Lessons
Other democracies have experienced similar institutional conflicts. The UK’s parliamentary sovereignty faces European Court challenges. Moreover, the US Supreme Court regularly clashes with congressional authority.
However, India’s situation remains unique due to its basic structure doctrine. This principle creates stronger judicial review powers than many democracies. Consequently, institutional tensions may prove more persistent here.
The Path Forward After Jagdeep Dhankhar’s Resignation
Dhankhar’s departure provides an opportunity for constitutional reflection and healing. His successor might adopt a more collaborative approach toward judicial relations. Moreover, institutional dialogue could replace confrontation going forward.
Potential Institutional Reforms : Jagdeep Dhankhar’s resignation
Various reform proposals could address underlying tensions between institutions. Clearer constitutional boundaries might reduce future conflicts. Moreover, formal consultation mechanisms could improve inter-institutional cooperation.
Some experts suggest constitutional conventions similar to Westminster systems. These informal rules could guide institutional behavior during conflicts. Furthermore, they might preserve democratic norms during partisan disagreements.
Lessons from Dhankhar’s Tenure
His presidency demonstrated both institutional vulnerabilities and strengths. While his criticism created tensions, democratic institutions survived the challenge. Moreover, judicial independence remained largely intact despite sustained pressure.
Future leaders might learn from both his mistakes and insights. Institutional respect requires balancing legitimate criticism with democratic cooperation. Furthermore, constitutional roles demand careful consideration of broader implications.
Check out more constitutional analysis at The Wire and detailed legal commentary at LiveLaw.
Conclusion: Legacy of Constitutional Questions
Jagdeep Dhankhar’s resignation marked the end of an extraordinary constitutional chapter. His persistent questioning of judicial authority challenged established norms significantly. Moreover, his criticism sparked important debates about institutional balance.
While his approach proved controversial, it highlighted legitimate constitutional concerns. The tension between parliamentary sovereignty and judicial review requires ongoing attention. Furthermore, democratic institutions must continuously evolve to serve public interests.
His legacy will likely influence future institutional relationships for years. Moreover, the questions he raised about NJAC and basic structure doctrine remain unresolved. Therefore, his impact on Indian constitutional discourse will persist long after his departure.
The balance between democratic accountability and constitutional protection remains delicate. Future leaders must navigate these tensions more carefully than Dhankhar did. However, his willingness to raise difficult questions contributed to important constitutional conversations.
Photo: Image of Jagdeep Dhankhar at official podium
Video: Dhankhar’s Parliamentary Speech on NJAC
Tweet: @VPIndia Official Tweet on Constitutional Matters








